Inactivation of microorganisms or surface functionalization of objects with variations in form and size by means of a cold plasma process.
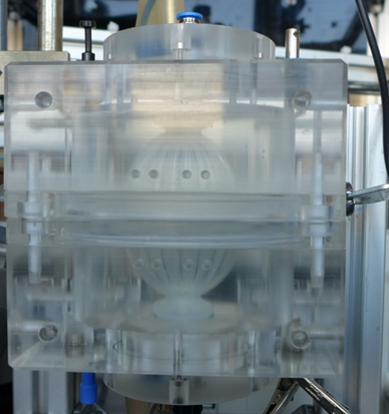
FEPS = Flexible Electrode Plasma Source (Treater)
Description of the technology
By means of flexible electrodes and an elastic dielectric, it is achieved that the discharge-forming structure of the device can fit closely to the material to be treated. This reduces the discharge gap and the impact distance to a minimum. This enables the use of low operating voltages and thus low-cost power supplies. The small discharge gap drastically reduces the costs for the operating gases. Expensive noble gases are only required to a small extent or, if the process permits, can also be replaced by compressed air.
Such a flexible arrangement is of particular advantage whenever the product to be treated has unavoidable variations in form and size, as occurs, for example, with natural products such as eggs.
Competitive procedure
-
Thermal treatment: The egg is heated briefly, sometimes several times with different times and temperatures, with the aim of preventing the egg white from coagulating but at the same time inactivating microbial infestation on the shell. However, since there is a possibility that microorganisms, such as salmonellae, can migrate into the interior of the egg and multiply there, eggs are also pasteurised on the inside at the Belgian manufacturing company Lodewijckx (https://www.cocovite.be/de/produkte/schaleneier/pasteurisierte-schaleneier) using steam. These products are mainly aimed at the care gastronomy sector. Since effective heat treatment always causes a change in the product, there are reservations about the use of the technology.
-
UV-C irradiation: A reduction of the microbial load by a power of ten is stated, which can, however, be significantly reduced by contamination, e.g. faeces.
-
In scientific publications, other methods such as ultrasound, hot water immersion and microwave irradiation are being investigated.
Advantage of our technology
- Most comparable to the UV-C treatment, but higher efficacy of approx. 3 lg
- Dry process
- No chemistry
- Required media such as electricity, compressed air are available
- Short treatment times
- Parallelizable
Opportunities for cooperation
We are looking for cooperation partners for the further development and industrialization of the presented process. In this case, cooperation with our institute is possible as an:
- Industrial partner for the application of funding and/or
- Partner for the further development of the process.
